20230326024500 - BLG - Alien Saboteaur - HTB Cyber Apocalyse 2023

Introduction
This challenge is a Virtual Machine (VM) based reversing challenge from Hack The Box CTF, Cyber Apocalypse 2023. This challenge requires participants to reverse engineer a simple custom instruction sets. In this challenge, the objective was to gain access to the main computer and shutdown the vessel. But to do so, access codes are required which is incidentally the flag for the challenge. The following image shows the description of the challenge. For this writeup, it is assumed that the reader has done some reversing on this binary. Therefore, this would include the important pointers and the script for solving the challenge.
In a Nutshell
To gain access to the main computer of the vessel in the Shutdown Sequence challenge, the keycode and secret code has to be supplied. To begin, two files were downloaded. One is the main binary which takes in an argument for a ROM like file which is responsible for running the custom virtual machine implemented in the challenge. Additionally, the gibberish, weird language described in the description refers to encrypted instructions which can be decrypted via a single byte XOR. Interestingly, the challenge incorporated an anti-debugging feature that attempted to detect when a debugger like GDB was attached via the ptrace syscall. For this challenge, I have written a minimal disassembler that emits pseudo assembly to aid in the reversing process.
The challenge in a nutshell consists of common and familiar instructions. They are
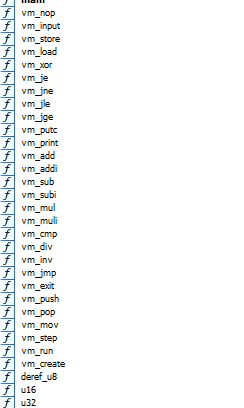
The following describes the VM in a high-level overview.
Challenge binary takes in a file containing instruction and other data.
A VM Context is created via
vm_createwhich contains: a. Registers b. Stack c. Stack Pointer d. Program Counter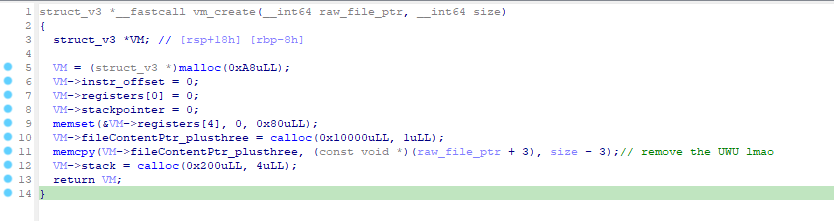
VM then run via the
vm_stepin a while loopEach instruction is 6 bytes in length with first byte as the opcode a. Opcode values are based on index of the opcode function table.
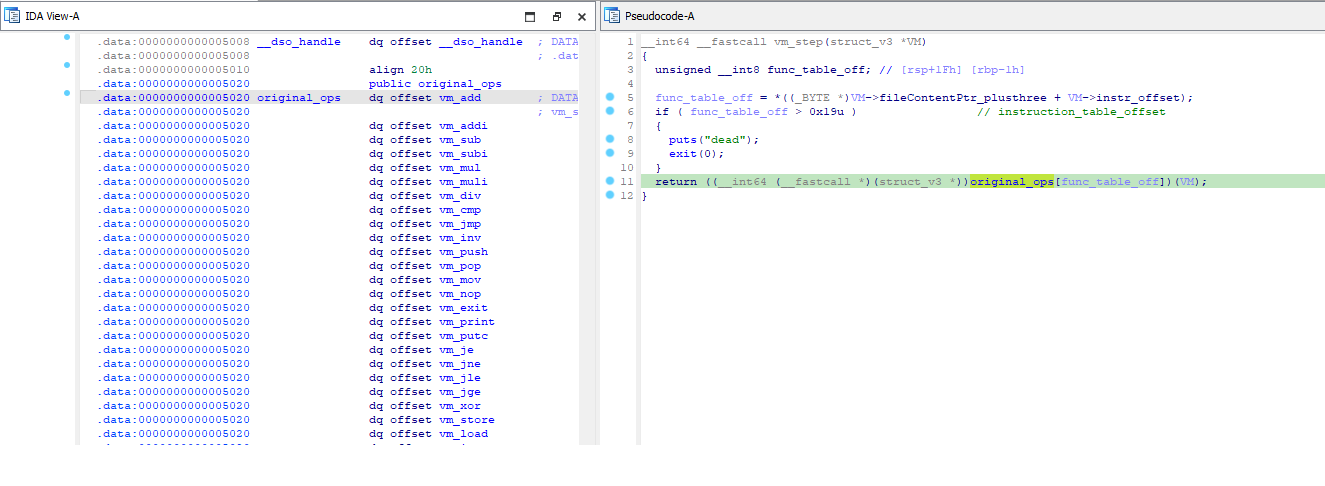
b. Instruction opcode ranges from 0x00 to 0x19
- The Virtual Machine ignores the first three bytes of the file. The rest are interpreted as Virtual Machine Instructions. a. First byte instruction starts at offset 3.
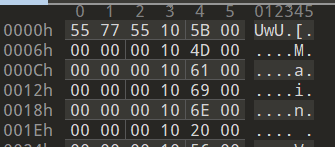
b. Example 1 : {10 4D 00 00 00 00} i. Opcode 0x10 maps to vm_putc which prints a character in the console. The next byte indicates the ASCII character M to print out. c. Example 2 : {0A 0f 00 00 00 00} i. Opcode 0x0A maps to vm_push. The next byte refers to the register whose value would be pushed onto the stack.
## Writing the Disassembler
To make it easier to analyze and reverse engineer, the first three bytes from the `bin` file was removed completely. The view of six bytes per row in the hex editor was set to make it easier to view the instructions.
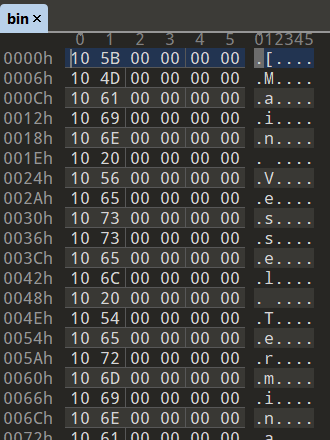
Familiarizing myself with the layouts and pattern in the decompiled code is definitely useful when writing the disassembler. The following few examples shows how the disassemblies were emited.
### Example Disassembly #1 – `vm_push`
```cstruct_v3 *__fastcall vm_push(struct_v3 *a1){ struct_v3 *result; // rax
*(4LL * a1->stackpointer++ + a1->stack) = *&a1->registers[4 * deref_u8(a1->fileContentPtr_plusthree + a1->instr_offset + 1) + 4]; result = a1; a1->instr_offset += 6; return result;}This instruction pushes a byte onto the stack from the register pointed to by the second byte in the instruction.
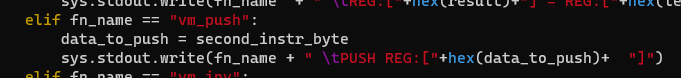
The following shows an example disassembly for this instruction.
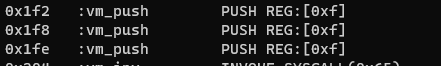
Example Disassembly #2 – vm_je
struct_v3 *__fastcall vm_je(struct_v3 *a1){ int v1; // edx struct_v3 *result; // rax int v3; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = *&a1->registers[4 * deref_u8(a1->fileContentPtr_plusthree + a1->instr_offset + 1) + 4]; if ( v3 == *&a1->registers[4 * deref_u8(a1->fileContentPtr_plusthree + a1->instr_offset + 2) + 4] ) { v1 = 6 * u16(a1->fileContentPtr_plusthree + a1->instr_offset + 3); result = a1; a1->instr_offset = v1; } else { result = a1; a1->instr_offset += 6; } return result;}The value of register pointed to by second byte of the instruction is checked against the value register pointed to by the third byte. If the values are equal, then the instr_offset or the instruction pointer is modified. Else, it would move to the next instruction. The following shows the code used for the disassembler to disassemble the vm_je operation in the VM.

The output is as follows:

Example Disassembly #3 – vm_inv (Anti-Debugging)
vm_inv refers to the INVocation of syscalls. The syscall number comes from the second byte of the instruction.
struct_v3 *__fastcall vm_inv(struct_v3 *a1){…… sysno = deref_u8(a1->fileContentPtr_plusthree + a1->instr_offset + 1); v1 = deref_u8(a1->fileContentPtr_plusthree + a1->instr_offset + 2); sysno_4 = v1; if ( v1 ) { stack = a1->stack; v3 = a1->stackpointer - 1; a1->stackpointer = v3; v4 = *(stack + 4LL * v3); } else { v4 = 0; } file_descriptor = v4; if ( sysno_4 <= 1 ) { v7 = 0; } else { v5 = a1->stack; v6 = a1->stackpointer - 1; a1->stackpointer = v6; v7 = *(v5 + 4LL * v6); } v15 = v7; if ( sysno_4 <= 2 ) { v10 = 0; } else { v8 = a1->stack; v9 = a1->stackpointer - 1; a1->stackpointer = v9; v10 = *(v8 + 4LL * v9); } *&a1->registers[128] = syscall(sysno, file_descriptor, v15, v10); result = a1; a1->instr_offset += 6; return result;}The following shows the code used for emiting the disassembly for the syscall invoke function.

And finally, the example output from the bin file:

The result of the syscall is stored in REG:[0x1f] which corresponds to *&a1->registers[0x80]. You can find the code of the disassembler in the appendix section at the end of this blog.
Dump and Analyze
This section covers the analysis after the initial disassembly.
Keycode Check
The following is the dumped disassembly of the keycode checking function
Disassembly
0x0 :vm_putc […<prints banner message>…0xf0 :vm_putc >0xf6 :vm_putc0xfc :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 f a00x102 :vm_mov REG[0x1c] = 0 0 00x108 :vm_mov REG[0x1d] = 0 0 110x10e :vm_input input to REG[0x19]0x114 :vm_store bin[REG[0x1e]] = REG[0x19]0x11a :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x10x120 :vm_addi REG[0x1c] = REG[0x1c] + 0x10x126 :vm_jle if REG[0x1c] <= REG[0x1d] then JMP bin[0x10e]0x12c :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 10 40x132 :vm_mov REG[0x1f] = 0 f a00x138 :vm_mov REG[0x1c] = 0 0 00x13e :vm_mov REG[0x1d] = 0 0 a0x144 :vm_mov REG[0x1b] = 0 0 a90x14a :vm_mov REG[0x17] = 0 0 00x150 :vm_load REG[0x19] = bin[REG[0x1e]]0x156 :vm_load REG[0x18] = bin[REG[0x1f]]0x15c :vm_xor REG:[0x19] = REG:[0x1b] ^ REG:[0x19]0x162 :vm_je IF REG:[0x19] == REG:[0x18] THEN JMP TO 0x1d40x168 :vm_putc U0x16e :vm_putc n0x174 :vm_putc k0x17a :vm_putc n0x180 :vm_putc o0x186 :vm_putc w0x18c :vm_putc n0x192 :vm_putc0x198 :vm_putc k0x19e :vm_putc e0x1a4 :vm_putc y0x1aa :vm_putc c0x1b0 :vm_putc o0x1b6 :vm_putc d0x1bc :vm_putc e0x1c2 :vm_putc !0x1c8 :vm_putc0x1ce :vm_exit0x1d4 :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x10x1da :vm_addi REG[0x1f] = REG[0x1f] + 0x10x1e0 :vm_addi REG[0x1c] = REG[0x1c] + 0x10x1e6 :vm_jle if REG[0x1c] <= REG[0x1d] then JMP bin[0x150]Keycode Check Overview
- User keycode is stored in memory location 0xfa0 (offset of the file as well)
- Keep getting user input till 0x11 bytes were stored
- Raw bytes are located at 0x1004
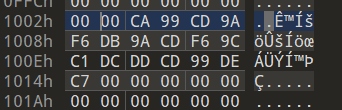
- XOR all the raw bytes with 0xA9
- If comparison fails at 0x162, then keycode is incorrect
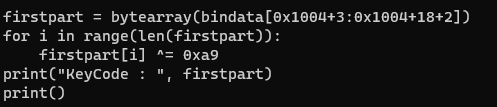
Keycode Retrieval
The key code c0d3_r3d_5hutd0wn is retrieved via a simple script.
Entering the key should bring us to the next stage. This is peculiar at first due to the absence of vm_putc instructions putting the Enter secret phrase string in the disassembled code.
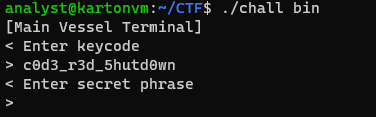
It should be noted that the output above is possible when a debugger is not attached to the process. This is what it would look like when GDB is attached to the process.
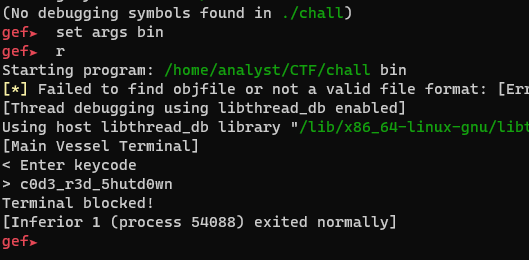
Anti-Debugging – Syscall PTRACE
This instruction is used to invoke the ptrace syscall number 0x65. This instruction is used only once in the entire bin file. This value is then used to compare to see if a debugger is present when debugging.
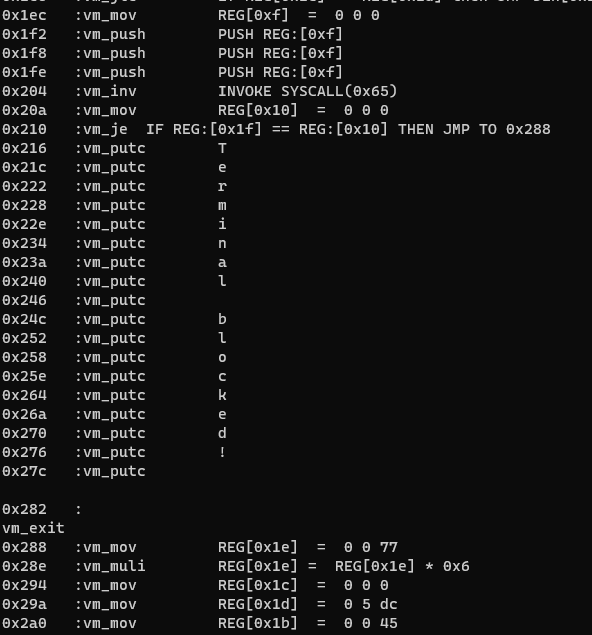
Anti-Debugging Bypass
Fortunately, patching of the bin file is sufficient:
- Patch the
vm_je(0x11) tovm_jne(0x12) - OPTIONALLY, The opcode 0x9 can optionally be be located and replaced with 0xd. a. 0xd corresponds to the VM’s NOP operation,
vm_nopb. We can also replace the three push statements as well
Bypass Script
f = open("./bin","rb")bindata = bytearray(f.read())f.close()bindata[0x213] = 0x12 # Change JE to JNEf = open("./bypass_bin","wb")f.write(bindata)f.close()The newly disassembled code demonstrating the successful patch.
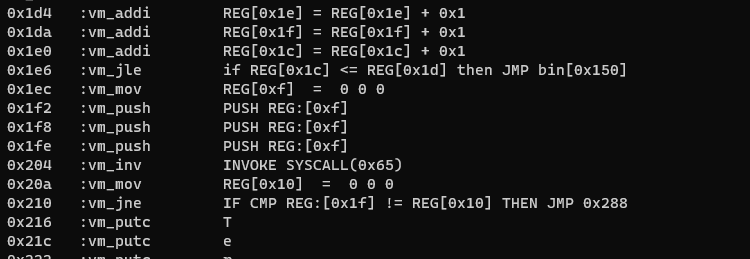
The patched bin file should successfully bypass the anti-debugging feature.
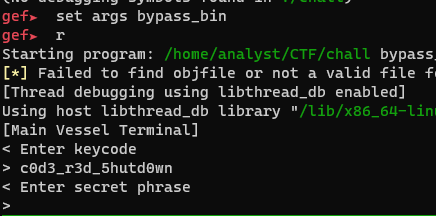
Decrypting the Next Stage
While it may be tempting to conclude the end of the challenge with the keycode, the second stage is present to bring us back from our dream. The following disassembly explains that there are more code.
Disassembly #1 - With Encrypted Instructions
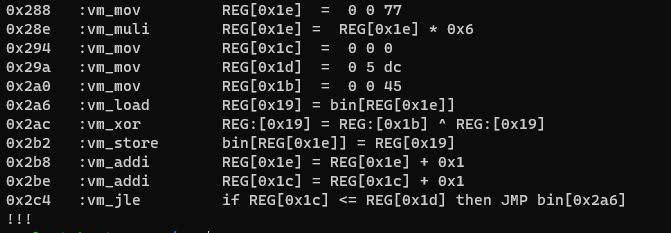
- Location of encrypted bytes are located at (0x77 * 0x6)= 0x2ca
- If the first three bytes of the bin file is not removed, then the offset would be 0x2cd.
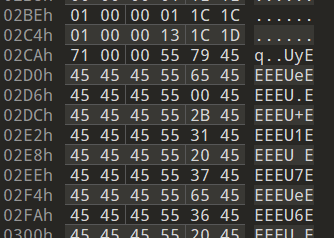
- The xor key is constant value of 0x45
- When 0x5dc bytes has been xor’d, it should continue on the the decrypted instructions.
The reason that the rest of the instructions are not present is due to the encrypted instructions containing opcode values larger than 0x19. To get the rest of the disassembly, we have to decrypt the values in the bin file.
Decrypting Script
# Assumes that the bin file contains the three ignored bytes
```pythonf = open("./bypass_bin","rb")bindata = bytearray(f.read())f.close()for i in range(len(bindata[0x2ca+3 : 0x591])): bindata[0x2ca+3+i] ^= 0x45f = open("./decrypted_bin","wb")f.write(bindata)f.close()historyDisassembly #2 – Instructions Decrypted
With the instructions properly decrypted, the prompt to enter secret phrase can be found.
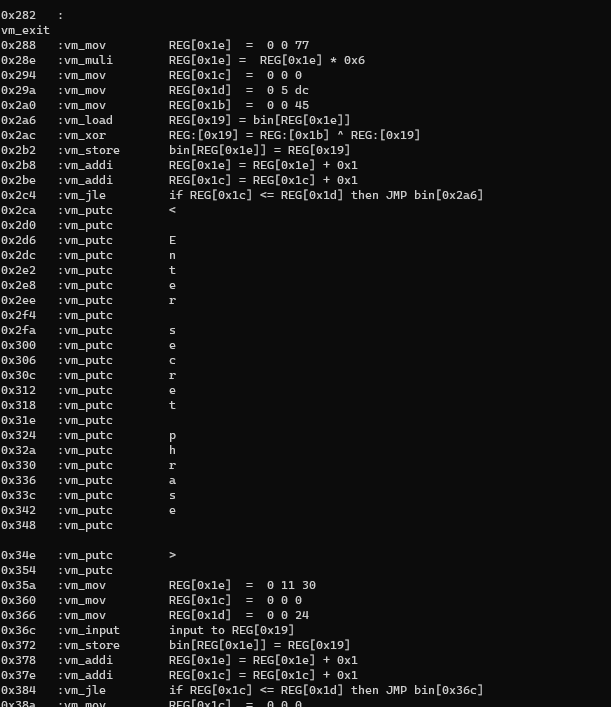
With this, further light can be shed on what algorithms is used to manipulate the secret phrase before comparing to a result bytearray.
Secret Phrase Recovery
This part will explain how the pass phrase input by user is manipulated and the operations can be reversed to retrieve the flag.
Algorithm of passphrase manipulation
The algorithm that was employed is not complicated.
- Pass phrase is stored into 0x1130 in file offset (without the ignored bytes)
- Length of passphrase is 0x24
- There exists a position-to-swap array which stores position to swap bytes with in the stored passphrase
- There exists a xor_key list which contains list of xor key values
- There exists a result list which contains values that the passphrase should contain after manipulation
- For each xor key, swapping is done via the position-to-swap array before xor’ing the values of manipulated pass phrase.
Disassembly of Algorithm
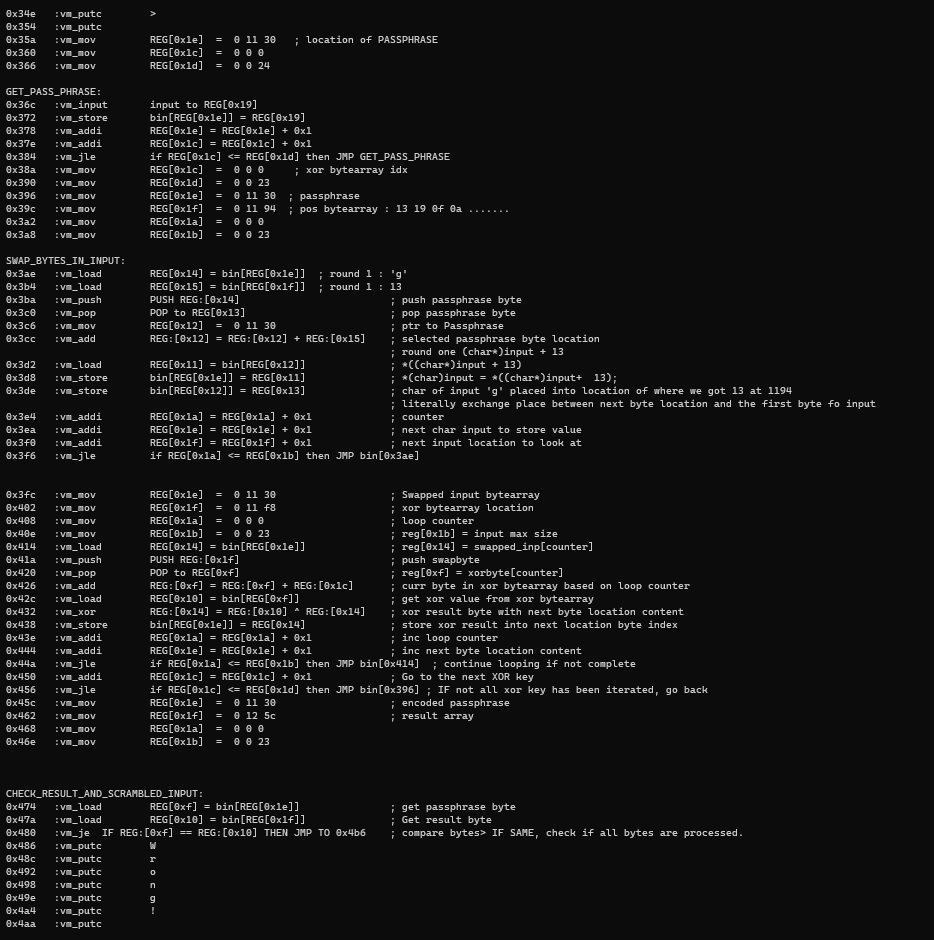
Pseudocode of Algorithm
The following presents the pseudocode of the algorithm for sanity
# Enter 0x24 bytespassphrase = bytearray(input("Enter secret phrase :"))
for j in range(len(xor_list)):
# Swap position for i in range(len(pos_list)): swap_position = pos_list[i] passphrase[i], passphrase[swap_position] = passphrase[swap_position], passphrase[i]
# Xor with key after swapping xor_key = xor_list[j] for k in range(len(passphrase)): passphrase[k] ^= xor_keyFlagging
Plan to flag
The plan is simple.
- Iterate through all xor keys
- For each xor key: a. undo the swap b. xor all the bytes of result list (end array) with the xor key
Script
f = open("bypass_bin","rb")bindata = f.read()f.close()
pos = bytearray(bindata[0x1194+3:0x11b8+3])xor_list = bytearray(bindata[0x11f8+3:0x121c+3])result_list = bytearray(bindata[0x125c+3:0x1280+3])
firstpart = bytearray(bindata[0x1004+3:0x1004+18+2])for i in range(len(firstpart)): firstpart[i] ^= 0xa9print("KeyCode : ", firstpart)
def restore(swapped_data, pos): for i in range(len(pos)-1, -1, -1): swapped_data[pos[i]], swapped_data[i] = swapped_data[i], swapped_data[pos[i]] return swapped_data
def solve(result_list, xor_list):
for i in range(len(xor_list)): xor_key= xor_list[i]
for j in range(len(result_list)): curr_byte = result_list[j] result_list[j] ^= xor_key result_list = restore(result_list,pos) print(result_list)
solve(result_list,xor_list)
"""KeyCode : bytearray(b'c0d3_r3d_5hutd0wn')bytearray(b'HTB{5w1rl_4r0und_7h3_4l13n_l4ngu4g3}')"""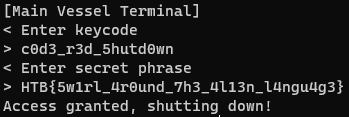
HTB{5w1rl_4r0und_7h3_4l13n_l4ngu4g3}
Appendix
Disassembler Code
import sys
s = """0000000000005020 original_ops dq offset vm_add.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_addi.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_sub.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_subi.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_mul.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_muli.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_div.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_cmp.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_jmp.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_inv.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_push.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_pop.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_mov.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_nop.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_exit.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_print.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_putc.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_je.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_jne.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_jle.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_jge.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_xor.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_store.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_load.data:0000000000005020 dq offset vm_input"""
instruction_offsets = []
for i in s.split("\n")[1:]: temp = "" if "offset" in i: temp = i.split("offset")[1] instruction_offsets.append(temp)
def read_bin(fname): f = open(fname,"rb") bin_data = f.read()[3:] f.close() return bin_data
function_set = set()function_set.add("vm_putc")
# First three UwU is not needed#data = read_bin("./bin")[3:]#data = read_bin("./bypass_bin")data = read_bin("./decrypted_bin")#data = read_bin("./deob_instr")[3:]#data = read_bin("./new_patch_bin")[3:]
for i in range(0,len(data),6): if data[i] >0x19: break fn_name = instruction_offsets[data[i]].strip() function_set.add(fn_name)
for i in range(0,len(data),6):
if data[i] > 0x19: break sys.stdout.write("\n" +hex(i) + "\t:")
fn_name = instruction_offsets[data[i]].strip() second_instr_byte = data[i+1] third_instr_byte = data[i+2] fourth_instr_byte = data[i+3] fifth_instr_byte = data[i+4] if fn_name == "vm_putc": sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \t" +chr(second_instr_byte )) elif fn_name == "vm_mov": src = hex(fifth_instr_byte)[2:]+" " + hex(fourth_instr_byte)[2:]+" " + hex(third_instr_byte)[2:] dest = second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tREG[" + hex(dest) + "] = " + src) elif fn_name == "vm_input": location_to_store_byte= second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tinput to REG[" + hex(location_to_store_byte) + "]") elif fn_name == "vm_store": offset = second_instr_byte data_to_store = third_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tbin[REG[" + hex(offset) + "]] = REG[" + hex(data_to_store) + "]") elif fn_name == "vm_addi": result = second_instr_byte reg = third_instr_byte imm = fourth_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tREG["+hex(result) + "] = REG["+ hex(reg) + "] + " + hex(imm) ) elif fn_name == "vm_jle": left = second_instr_byte right = third_instr_byte jump_location = hex(int(hex(fifth_instr_byte)[2:] + hex(fourth_instr_byte)[2:] , 16)*6) sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tif REG[" + hex(left) + "] <= REG[" + hex(right) + "] then JMP bin[" + jump_location + "]") elif fn_name == "vm_muli": reg = third_instr_byte imm = fourth_instr_byte dest = second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tREG[" + hex(dest) + "] = REG[" + hex(reg) + "] * " + hex(imm)) elif fn_name == "vm_exit": sys.stdout.write("\n" + fn_name) elif fn_name == "vm_load": dest = second_instr_byte data_to_load = third_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tREG[" + hex(dest) + "] = bin[" + "REG["+ hex(data_to_load)+ "]] ") elif fn_name == "vm_xor": right = third_instr_byte left = fourth_instr_byte result = second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tREG:["+hex(result)+"] = REG:["+hex(left) + "] ^ REG:["+hex(right)+"]") elif fn_name == "vm_push": data_to_push = second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tPUSH REG:["+hex(data_to_push)+ "]") elif fn_name == "vm_inv": sysno = second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tINVOKE SYSCALL(" + hex(sysno) + ")") elif fn_name == "vm_je": left = second_instr_byte right = third_instr_byte jump_location = hex(int(hex(fifth_instr_byte)[2:] + hex(fourth_instr_byte)[2:] , 16)*6) sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tIF REG:[" + hex(left) + "] == REG:[" + hex(right) + "] THEN JMP TO "+ jump_location) elif fn_name == "vm_pop": popped_data = second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tPOP to REG["+hex(popped_data) + "]") elif fn_name == "vm_print": to_print = second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tPRINT REG["+hex(to_print) + "]") elif fn_name == "vm_jne": first = second_instr_byte second = third_instr_byte jump_location = hex(int(hex(fifth_instr_byte)[2:] + hex(fourth_instr_byte)[2:] , 16)*6) sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tIF CMP REG:["+hex(first) + "] != REG["+hex(second) + "] THEN JMP " + jump_location) elif fn_name == "vm_add": left = third_instr_byte right = fourth_instr_byte result = second_instr_byte sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " \tREG:["+hex(result) + "] = REG:["+hex(left) + "] + REG:[" + hex(right) + "] ") elif fn_name == "vm_nop": sys.stdout.write(fn_name) else: sys.stdout.write(fn_name + " : not implemented ") continue if fn_name in function_set: function_set.remove(fn_name)
print()
print("!!!")for i in function_set: print(i)Output Disassembly (patched and decrypted)
0x0 :vm_putc [0x6 :vm_putc M0xc :vm_putc a0x12 :vm_putc i0x18 :vm_putc n0x1e :vm_putc0x24 :vm_putc V0x2a :vm_putc e0x30 :vm_putc s0x36 :vm_putc s0x3c :vm_putc e0x42 :vm_putc l0x48 :vm_putc0x4e :vm_putc T0x54 :vm_putc e0x5a :vm_putc r0x60 :vm_putc m0x66 :vm_putc i0x6c :vm_putc n0x72 :vm_putc a0x78 :vm_putc l0x7e :vm_putc ]0x84 :vm_putc
0x8a :vm_putc <0x90 :vm_putc0x96 :vm_putc E0x9c :vm_putc n0xa2 :vm_putc t0xa8 :vm_putc e0xae :vm_putc r0xb4 :vm_putc0xba :vm_putc k0xc0 :vm_putc e0xc6 :vm_putc y0xcc :vm_putc c0xd2 :vm_putc o0xd8 :vm_putc d0xde :vm_putc e0xe4 :vm_putc0xea :vm_putc
0xf0 :vm_putc >0xf6 :vm_putc0xfc :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 f a00x102 :vm_mov REG[0x1c] = 0 0 00x108 :vm_mov REG[0x1d] = 0 0 110x10e :vm_input input to REG[0x19] ; Store user input0x114 :vm_store bin[REG[0x1e]] = REG[0x19] ; store into location 0xFA00x11a :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x10x120 :vm_addi REG[0x1c] = REG[0x1c] + 0x10x126 :vm_jle if REG[0x1c] <= REG[0x1d] then JMP bin[0x10e]0x12c :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 10 40x132 :vm_mov REG[0x1f] = 0 f a0 ; Location of user input0x138 :vm_mov REG[0x1c] = 0 0 00x13e :vm_mov REG[0x1d] = 0 0 a0x144 :vm_mov REG[0x1b] = 0 0 a90x14a :vm_mov REG[0x17] = 0 0 00x150 :vm_load REG[0x19] = bin[REG[0x1e]] ; 0x19 contain bytes in memroy0x156 :vm_load REG[0x18] = bin[REG[0x1f]] ; pointer to userinput0x15c :vm_xor REG:[0x19] = REG:[0x1b] ^ REG:[0x19] ; 0xa9 & memory0x162 :vm_jne IF CMP REG:[0x19] != REG[0x18] THEN JMP 0x1d4 ; compare if they are the same0x168 :vm_putc U0x16e :vm_putc n0x174 :vm_putc k0x17a :vm_putc n0x180 :vm_putc o0x186 :vm_putc w0x18c :vm_putc n0x192 :vm_putc0x198 :vm_putc k0x19e :vm_putc e0x1a4 :vm_putc y0x1aa :vm_putc c0x1b0 :vm_putc o0x1b6 :vm_putc d0x1bc :vm_putc e0x1c2 :vm_putc !0x1c8 :vm_putc
0x1ce :vm_exit0x1d4 :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x10x1da :vm_addi REG[0x1f] = REG[0x1f] + 0x10x1e0 :vm_addi REG[0x1c] = REG[0x1c] + 0x10x1e6 :vm_jle if REG[0x1c] <= REG[0x1d] then JMP bin[0x150]0x1ec :vm_mov REG[0xf] = 0 0 00x1f2 :vm_nop0x1f8 :vm_nop0x1fe :vm_nop0x204 :vm_nop0x20a :vm_mov REG[0x10] = 0 0 00x210 :vm_jne IF CMP REG:[0x1f] != REG[0x10] THEN JMP 0x2880x216 :vm_putc T0x21c :vm_putc e0x222 :vm_putc r0x228 :vm_putc m0x22e :vm_putc i0x234 :vm_putc n0x23a :vm_putc a0x240 :vm_putc l0x246 :vm_putc0x24c :vm_putc b0x252 :vm_putc l0x258 :vm_putc o0x25e :vm_putc c0x264 :vm_putc k0x26a :vm_putc e0x270 :vm_putc d0x276 :vm_putc !0x27c :vm_putc
0x282 :vm_exit0x288 :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 0 770x28e :vm_muli REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] * 0x60x294 :vm_mov REG[0x1c] = 0 0 00x29a :vm_mov REG[0x1d] = 0 5 dc0x2a0 :vm_mov REG[0x1b] = 0 0 450x2a6 :vm_load REG[0x19] = bin[REG[0x1e]]0x2ac :vm_nop0x2b2 :vm_store bin[REG[0x1e]] = REG[0x19]0x2b8 :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x10x2be :vm_addi REG[0x1c] = REG[0x1c] + 0x10x2c4 :vm_jle if REG[0x1c] <= REG[0x1d] then JMP bin[0x2a6]0x2ca :vm_putc <0x2d0 :vm_putc0x2d6 :vm_putc E0x2dc :vm_putc n0x2e2 :vm_putc t0x2e8 :vm_putc e0x2ee :vm_putc r0x2f4 :vm_putc0x2fa :vm_putc s0x300 :vm_putc e0x306 :vm_putc c0x30c :vm_putc r0x312 :vm_putc e0x318 :vm_putc t0x31e :vm_putc0x324 :vm_putc p0x32a :vm_putc h0x330 :vm_putc r0x336 :vm_putc a0x33c :vm_putc s0x342 :vm_putc e0x348 :vm_putc
0x34e :vm_putc >0x354 :vm_putc0x35a :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 11 30 ; location of PASSPHRASE0x360 :vm_mov REG[0x1c] = 0 0 00x366 :vm_mov REG[0x1d] = 0 0 24
GET_PASS_PHRASE:0x36c :vm_input input to REG[0x19]0x372 :vm_store bin[REG[0x1e]] = REG[0x19]0x378 :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x10x37e :vm_addi REG[0x1c] = REG[0x1c] + 0x10x384 :vm_jle if REG[0x1c] <= REG[0x1d] then JMP GET_PASS_PHRASE0x38a :vm_mov REG[0x1c] = 0 0 0 ; xor bytearray idx0x390 :vm_mov REG[0x1d] = 0 0 230x396 :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 11 30 ; passphrase0x39c :vm_mov REG[0x1f] = 0 11 94 ; pos bytearray : 13 19 0f 0a .......0x3a2 :vm_mov REG[0x1a] = 0 0 00x3a8 :vm_mov REG[0x1b] = 0 0 23
SWAP_BYTES_IN_INPUT:0x3ae :vm_load REG[0x14] = bin[REG[0x1e]] ; round 1 : 'g'0x3b4 :vm_load REG[0x15] = bin[REG[0x1f]] ; round 1 : 130x3ba :vm_push PUSH REG:[0x14] ; push passphrase byte0x3c0 :vm_pop POP to REG[0x13] ; pop passphrase byte0x3c6 :vm_mov REG[0x12] = 0 11 30 ; ptr to Passphrase0x3cc :vm_add REG:[0x12] = REG:[0x12] + REG:[0x15] ; selected passphrase byte location ; round one (char*)input + 130x3d2 :vm_load REG[0x11] = bin[REG[0x12]] ; *((char*)input + 13)0x3d8 :vm_store bin[REG[0x1e]] = REG[0x11] ; *(char)input = *((char*)input+ 13);0x3de :vm_store bin[REG[0x12]] = REG[0x13] ; char of input 'g' placed into location of where we got 13 at 1194 ; literally exchange place between next byte location and the first byte fo input0x3e4 :vm_addi REG[0x1a] = REG[0x1a] + 0x1 ; counter0x3ea :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x1 ; next char input to store value0x3f0 :vm_addi REG[0x1f] = REG[0x1f] + 0x1 ; next input location to look at0x3f6 :vm_jle if REG[0x1a] <= REG[0x1b] then JMP bin[0x3ae]
0x3fc :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 11 30 ; Swapped input bytearray0x402 :vm_mov REG[0x1f] = 0 11 f8 ; xor bytearray location0x408 :vm_mov REG[0x1a] = 0 0 0 ; loop counter0x40e :vm_mov REG[0x1b] = 0 0 23 ; reg[0x1b] = input max size0x414 :vm_load REG[0x14] = bin[REG[0x1e]] ; reg[0x14] = swapped_inp[counter]0x41a :vm_push PUSH REG:[0x1f] ; push swapbyte0x420 :vm_pop POP to REG[0xf] ; reg[0xf] = xorbyte[counter]0x426 :vm_add REG:[0xf] = REG:[0xf] + REG:[0x1c] ; curr byte in xor bytearray based on loop counter0x42c :vm_load REG[0x10] = bin[REG[0xf]] ; get xor value from xor bytearray0x432 :vm_xor REG:[0x14] = REG:[0x10] ^ REG:[0x14] ; xor result byte with next byte location content0x438 :vm_store bin[REG[0x1e]] = REG[0x14] ; store xor result into next location byte index0x43e :vm_addi REG[0x1a] = REG[0x1a] + 0x1 ; inc loop counter0x444 :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x1 ; inc next byte location content0x44a :vm_jle if REG[0x1a] <= REG[0x1b] then JMP bin[0x414] ; continue looping if not complete0x450 :vm_addi REG[0x1c] = REG[0x1c] + 0x1 ; Go to the next XOR key0x456 :vm_jle if REG[0x1c] <= REG[0x1d] then JMP bin[0x396] ; IF not all xor key has been iterated, go back0x45c :vm_mov REG[0x1e] = 0 11 30 ; encoded passphrase0x462 :vm_mov REG[0x1f] = 0 12 5c ; result array0x468 :vm_mov REG[0x1a] = 0 0 00x46e :vm_mov REG[0x1b] = 0 0 23
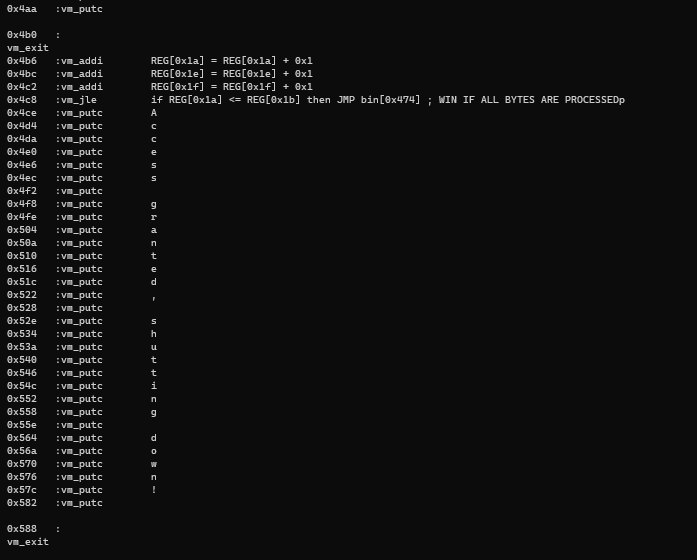
CHECK_RESULT_AND_SCRAMBLED_INPUT:0x474 :vm_load REG[0xf] = bin[REG[0x1e]] ; get passphrase byte0x47a :vm_load REG[0x10] = bin[REG[0x1f]] ; Get result byte0x480 :vm_je IF REG:[0xf] == REG:[0x10] THEN JMP TO 0x4b6 ; compare bytes> IF SAME, check if all bytes are processed.0x486 :vm_putc W0x48c :vm_putc r0x492 :vm_putc o0x498 :vm_putc n0x49e :vm_putc g0x4a4 :vm_putc !0x4aa :vm_putc
0x4b0 :vm_exit0x4b6 :vm_addi REG[0x1a] = REG[0x1a] + 0x10x4bc :vm_addi REG[0x1e] = REG[0x1e] + 0x10x4c2 :vm_addi REG[0x1f] = REG[0x1f] + 0x10x4c8 :vm_jle if REG[0x1a] <= REG[0x1b] then JMP bin[0x474] ; WIN IF ALL BYTES ARE PROCESSEDp0x4ce :vm_putc A0x4d4 :vm_putc c0x4da :vm_putc c0x4e0 :vm_putc e0x4e6 :vm_putc s0x4ec :vm_putc s0x4f2 :vm_putc0x4f8 :vm_putc g0x4fe :vm_putc r0x504 :vm_putc a0x50a :vm_putc n0x510 :vm_putc t0x516 :vm_putc e0x51c :vm_putc d0x522 :vm_putc ,0x528 :vm_putc0x52e :vm_putc s0x534 :vm_putc h0x53a :vm_putc u0x540 :vm_putc t0x546 :vm_putc t0x54c :vm_putc i0x552 :vm_putc n0x558 :vm_putc g0x55e :vm_putc0x564 :vm_putc d0x56a :vm_putc o0x570 :vm_putc w0x576 :vm_putc n0x57c :vm_putc !0x582 :vm_putc
0x588 :vm_exit0x58e :vm_add REG:[0x0] = REG:[0x0] + REG:[0x0]0x594 :vm_add REG:[0x0] = REG:[0x0] + REG:[0x0]0x59a :vm_add REG:[0x0] = REG:[0x0] + REG:[0x0]......